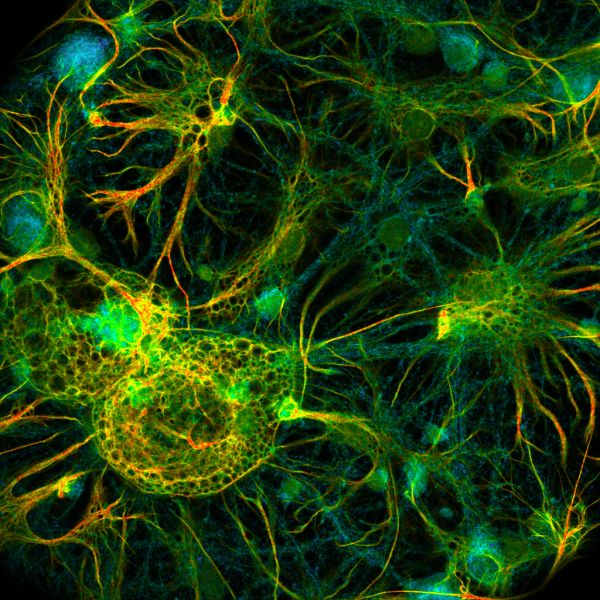
41 fluorescent labels and light microscopy
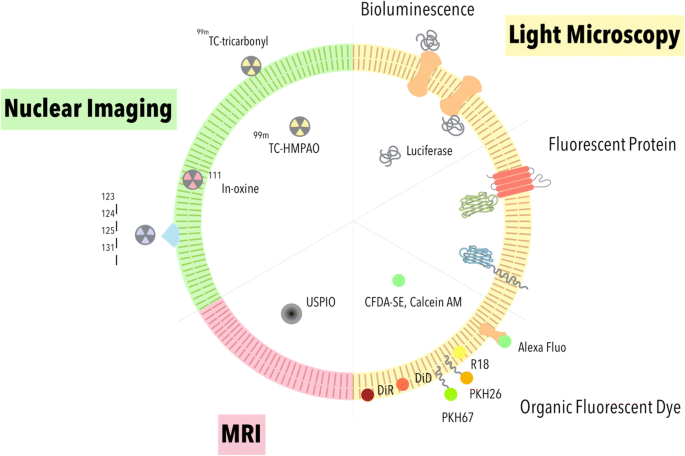
Dots, Probes and Proteins: Fluorescent Labels for Microscopy and Imaging There are currently 20 AlexaFluor dyes which span the excitation spectrum from 346 nm to 784 nm and are available as labelling kits, or conjugated to primary or secondary antibodies. Thermo Scientific produce their own probes called ' DyLight '. The ten probes which are currently available cover a spectrum from 350 nm to 800 nm. Fluorescence - Wikipedia Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation.It is a form of luminescence.In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, than the absorbed radiation.A perceptible example of fluorescence occurs when the absorbed radiation is in the ultraviolet region of the …
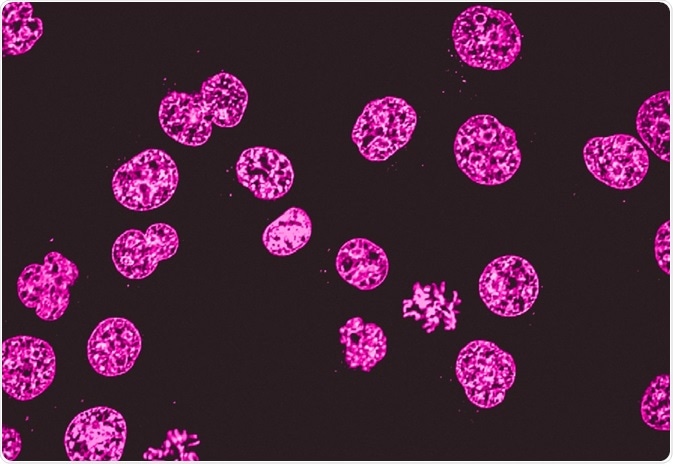
Novel Fluorescent Label Shines a Light on DNA Structure in Cancer Cells Novel Fluorescent Label Shines a Light on DNA Structure in Cancer Cells March 7, 2022 Researchers have developed a new fluorescent label that gives a clearer picture of how DNA architecture is...
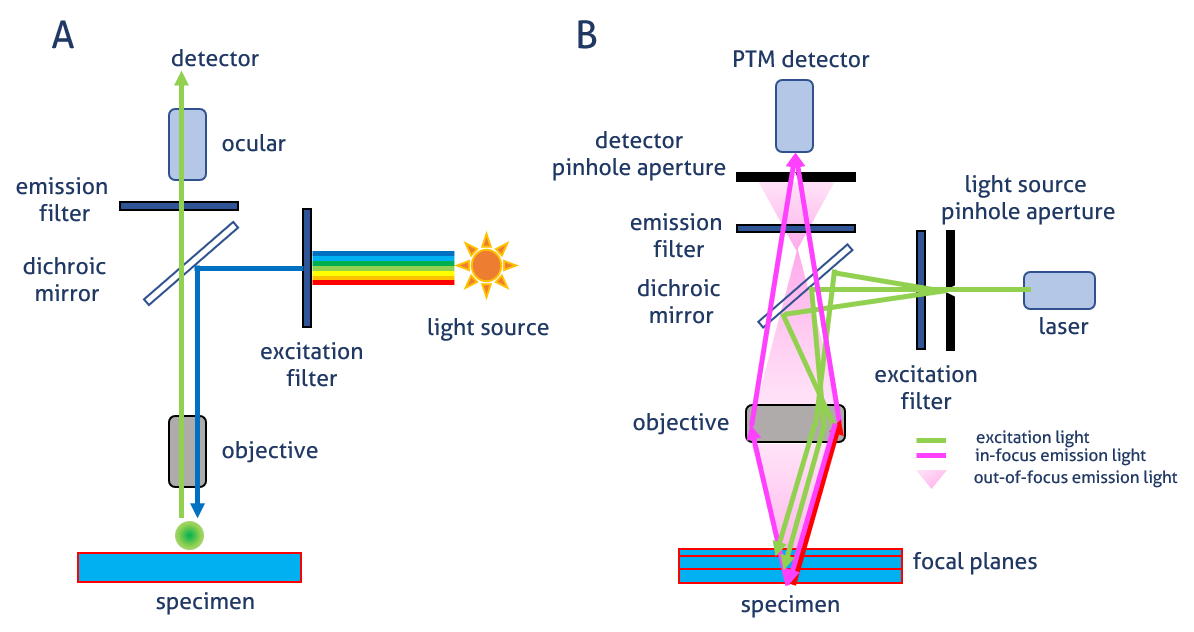
Fluorescent labels and light microscopy
PDF Direct Evidence of Lack of Colocalisation of Fluorescently Labelled ... Fluorescently labelled nanoparticles are routinely used in Correlative Light Electron Microscopy (CLEM) to combine the capabilities of two separate microscope platforms: fluorescent light microscopy (LM) and electron microscopy (EM). The inherent assumption is that the fluorescent label observed under LM colocalises well with the electron dense ... Imaging Flies by Fluorescence Microscopy: Principles, Technologies, and ... The development of fluorescent labels and powerful imaging technologies in the last two decades has revolutionized the field of fluorescence microscopy, which is now widely used in diverse scientific fields from biology to biomedical and materials science. ... has brought about the era of fluorescence light microscopy. The first fluorescence ... PDF In Silico Labeling: Predicting Fluorescent Labels in Unlabeled Images The z-stacks of transmitted-light microscopy images were acquired with different methods for enhancing contrast in unlabeled images. Several different fluorescent labels were used to generate fluorescence images and were varied between training examples; the checkerboard images indicate fluorescent labels that were not acquired for a given example.
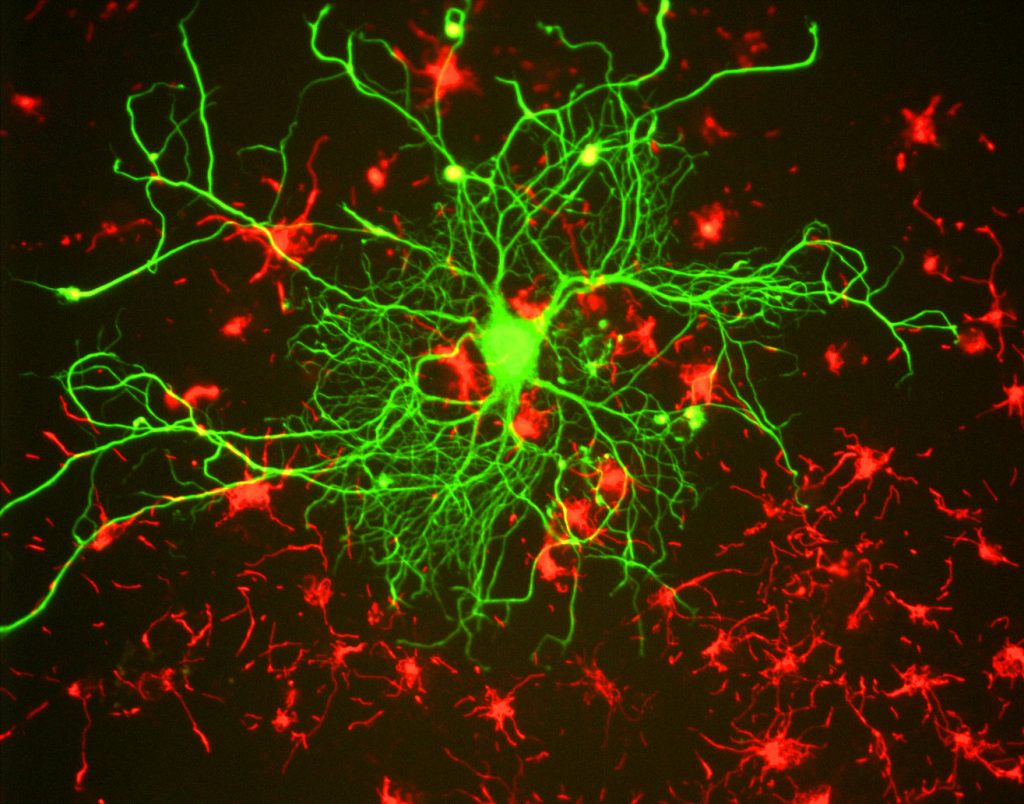
Fluorescent labels and light microscopy. Fluorescent Nanoparticles for Super-Resolution Imaging Super-resolution imaging techniques that overcome the diffraction limit of light have gained wide popularity for visualizing cellular structures with nanometric resolution. Following the pace of hardware developments, the availability of new fluorescent probes with superior properties is becoming ever more important. In this context, fluorescent nanoparticles (NPs) have attracted … Mica | Products | Leica Microsystems The Microhub enables you to simultaneously capture all 4 labels or different structures in a single acquisition for both widefield and confocal, ... Mica unifies transmitted and fluorescence light imaging modalities. ... This key application shows how Mica is used with fluorescent multi-well plate assays around Caspase 3/7 activations in apoptosis. Different Ways to Add Fluorescent Labels - Thermo Fisher Scientific Using fluorescence provides greater contrast compared to viewing your samples with brightfield microscopy alone. Labeling various targets with separate fluorescent colors allows you to visualize different structures or proteins within a cell in the same experiment. Labeling Proteins For Single Molecule Imaging - Teledyne Photometrics A fluorescent signal allows a protein's precise location to be determined as well as its behavior to be observed. This can then be studied in relation to other fluorescently tagged proteins. In this way, researchers are able to use fluorescence microscopy to visualize underlying biological processes.
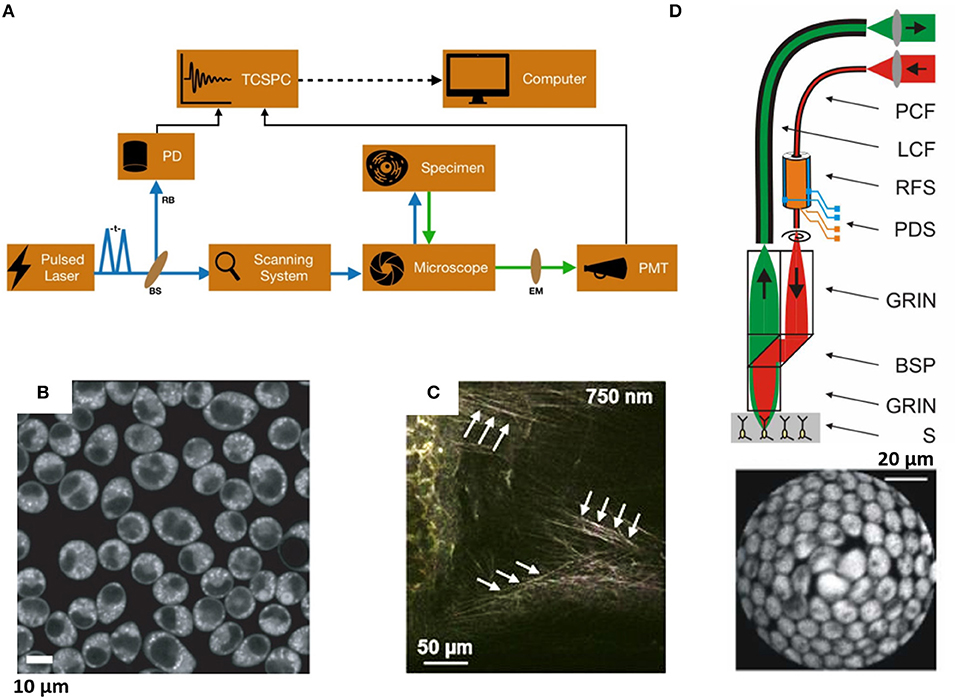
Light-sheet microscopy | sguenther.eu In biological research fluorescent microscopy is a widespread technique to get dynamic information about living systems. In order to obtain images specimen need to be labeled with fluorescent dyes or fluorescent proteins. During microscope recordings the specimen and their labels are excited with light of a certain wave length (color). Labeling the ER for Light and Fluorescence Microscopy Most of them are not 100% specific for the ER membrane and may label other organelles at varying concentrations and incubation times. ... C., Wang, P., Kriechbaumer, V. (2018). Labeling the ER for Light and Fluorescence Microscopy. In: Hawes, C., Kriechbaumer, V. (eds) The Plant Endoplasmic Reticulum . Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1691 ... Fluorescence Microscopy & Cell Imaging | Research | UNM Cancer Center Fluorescence microscopy is routinely used to determine spatial and topological information about cells and tissues. Sophisticated laser scanning microscopic instrumentation, ultra sensitive digital cameras and specialized fluorescence probes make it possible to visualize cellular events in real time down to the molecular level. ZEISS LSM 980 with Airyscan 2 NIR fluorescent labels are less phototoxic for living samples due to the longer wavelength. This allows you to investigate living samples for longer periods of time while limiting the influence of light. Additionally, light of longer wavelength ranges is less scattered by the sample tissue, increasing penetration depth.
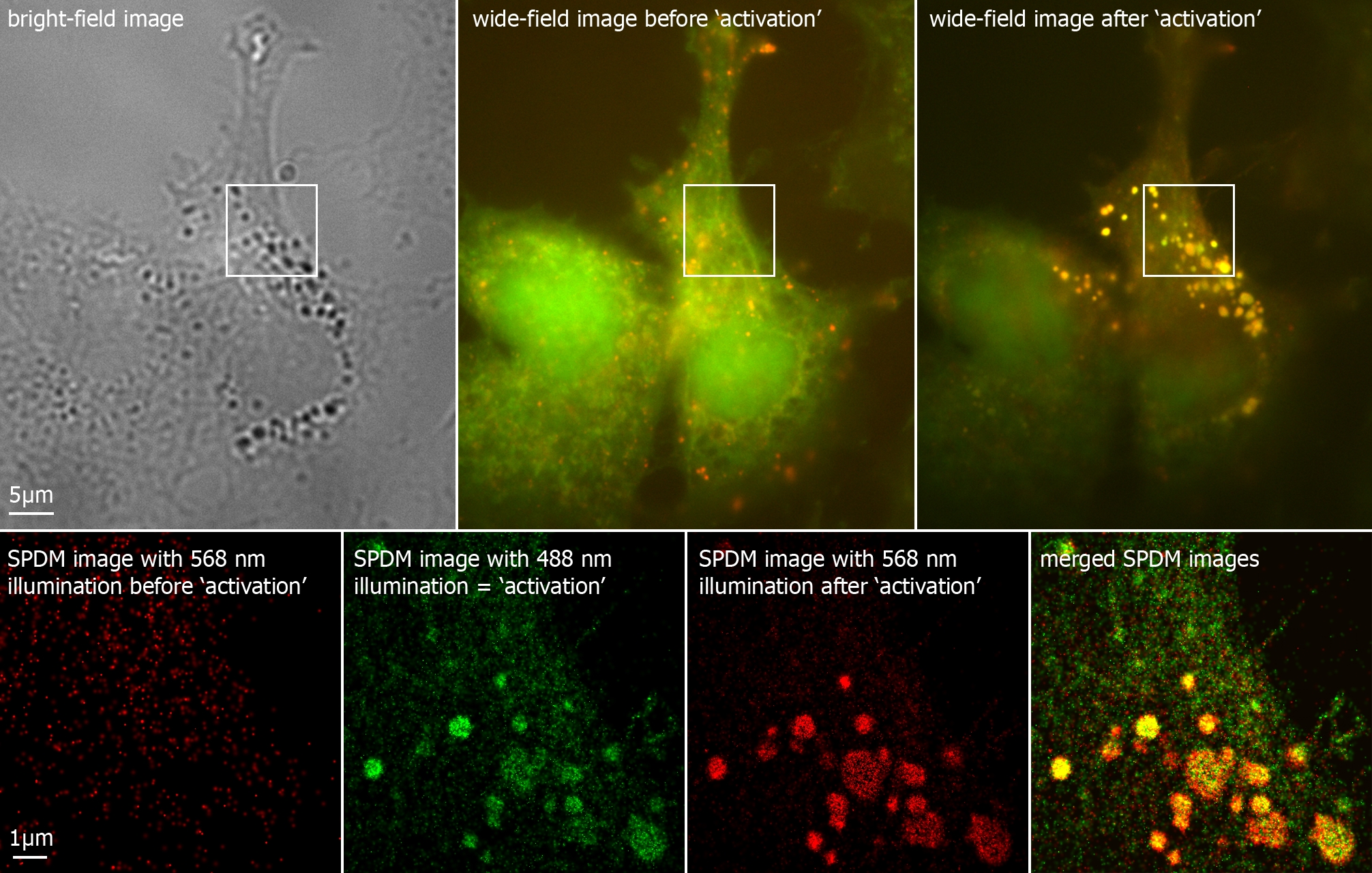
Fluorescent labeling of abundant reactive entities (FLARE) for cleared ... Fluorescence microscopy is a technique that is commonly used in the biomedical sciences. It offers the powerful ability to visualize structures or molecules in three dimensions within biological... Introduction to Fluorescence Microscopy • iBiology In this introductory lecture on light microscopy, Dr. Nico Stuurman describes the principles and properties of fluorescence microscopy. Skip to primary navigation; ... 00:01:04;23 so we label microtubules with the fluorescent dye 00:01:08;13 and we have part of the cell labeled in red, 00:01:11;25 and that part is actually the uh, nucleus Light Sheet Fluorescence Microscopy - an overview - ScienceDirect Light-sheet fluorescence microscopy, to the same extent as laser scanning confocal microscopy, now refers to a wide range of microscope systems (Figure 8.2) ... it is worth mentioning that it is the fluorescent label that is imaged and not the molecule of interest itself. It is therefore important to quantify the specificity and efficiency of ... Researchers demonstrate label-free super-resolution microscopy - Phys.org A newly developed sub-diffraction-limit microscopy approach doesn't require fluorescent labels. The video shows the process of the data evaluation algorithm, retrieving the positions and sizes of...
Label-free prediction of three-dimensional fluorescence images from ... We present a label-free method for predicting three-dimensional fluorescence directly from transmitted-light images and demonstrate that it can be used to generate multi-structure, integrated...
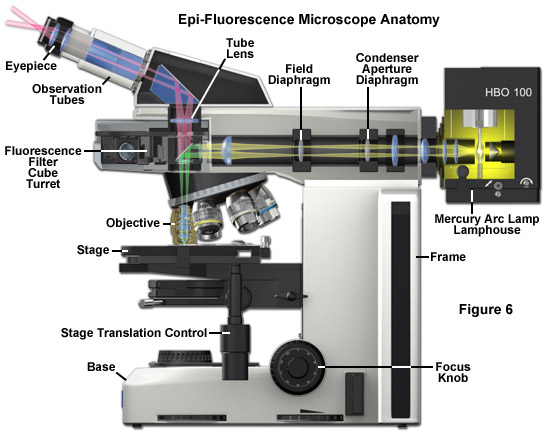
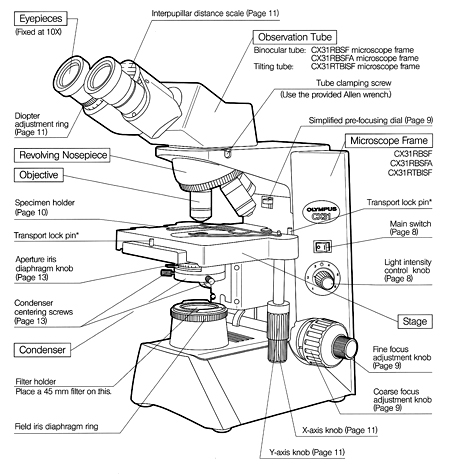
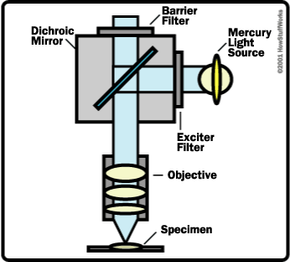
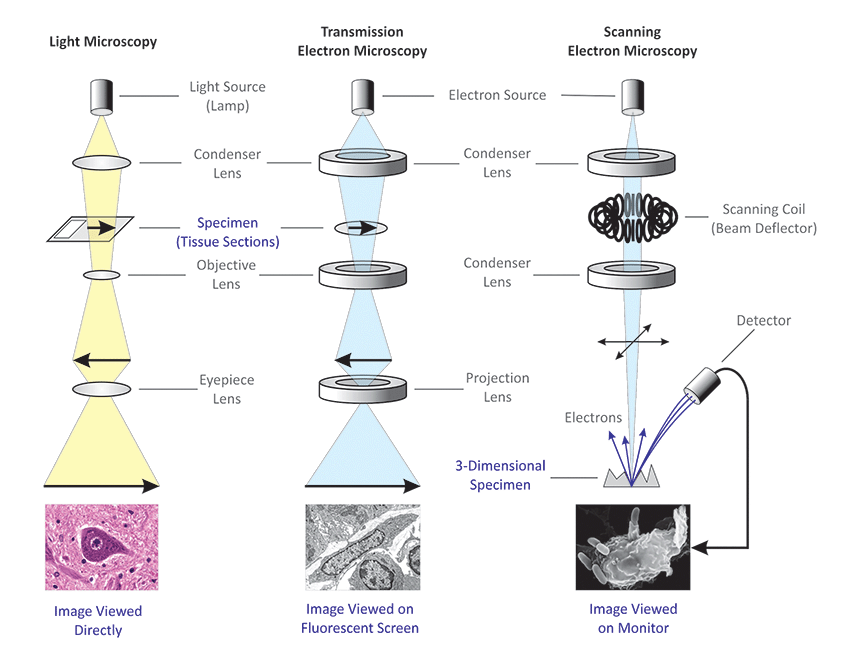
Light Microscope- Definition, Principle, Types, Parts, Labeled Diagram ... A light microscope is a biology laboratory instrument or tool, that uses visible light to detect and magnify very small objects and enlarge them. They use lenses to focus light on the specimen, magnifying it thus producing an image. The specimen is normally placed close to the microscopic lens.
Fluorescent Dyes | Science Lab | Leica Microsystems A basic principle in fluorescence microscopy is the highly specific visualization of cellular components with the help of a fluorescent agent. This can be a fluorescent protein - for example GFP - genetically linked to the protein of interest. If cloning is impossible - for instance in histologic samples - techniques such as immunofluorescence staining are used to visualize the protein ...
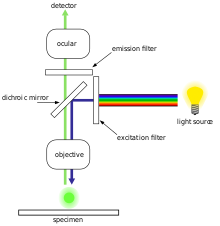
Fluorescence Microscopy - Explanation and Labelled Images Fluorescence microscopy uses a high-intensity light source that excites a fluorescent molecule called a fluorophore in the sample observed. The samples are labeled with fluorophore where they absorb the high-intensity light from the source and emit a lower energy light of longer wavelength.
mNeonGreen :: Fluorescent Protein Database 30.9.2021 · mNeonGreen is a basic (constitutively fluorescent) green/yellow fluorescent protein published in 2013, derived from Branchiostoma lanceolatum. It is reported to be a very rapidly-maturing monomer with moderate acid sensitivity.
In Silico Labeling: Predicting Fluorescent Labels in Unlabeled Images Microscopy is a central method in life sciences. Many popular methods, such as antibody labeling, are used to add physical fluorescent labels to specific cellular constituents. ... (ISL), reliably predicts some fluorescent labels from transmitted-light images of unlabeled fixed or live biological samples. ISL predicts a range of labels, such as ...
Fluorescence Microscope: Principle, Types, Applications Fluorescence microscopy is a light microscope that works on the principle of fluorescence. A substance is said to be fluorescent when it absorbs the energy of invisible shorter wavelength radiation (such as UV light) and emits longer wavelength radiation of visible light (such as green or red light). This phenomenon, also called fluorescence ...
In Silico Labeling: Predicting Fluorescent Labels in Unlabeled ... - Cell Fluorescence microscopy images can be predicted from transmitted-light z stacks • 7 fluorescent labels were validated across three labs, modalities, and cell types • New labels can be predicted using minimal additional training data Summary Microscopy is a central method in life sciences.
Fluorescent Labeling - What You Should Know - PromoCell Fluorescence microscopy allows the identification of cells and cellular components and the monitoring of cell physiology with high specificity. Fluorescence microscopy separates emitted light from excitation light using optical filters. The use of two indicators also allows the simultaneous observation of different biomolecules at the same time.
New fluorescent label provides a clearer picture of how DNA ... Unlike traditional fluorescence microscopy, which uses labels that glow constantly, this approach involves switching on only a subset of the labels at each moment.
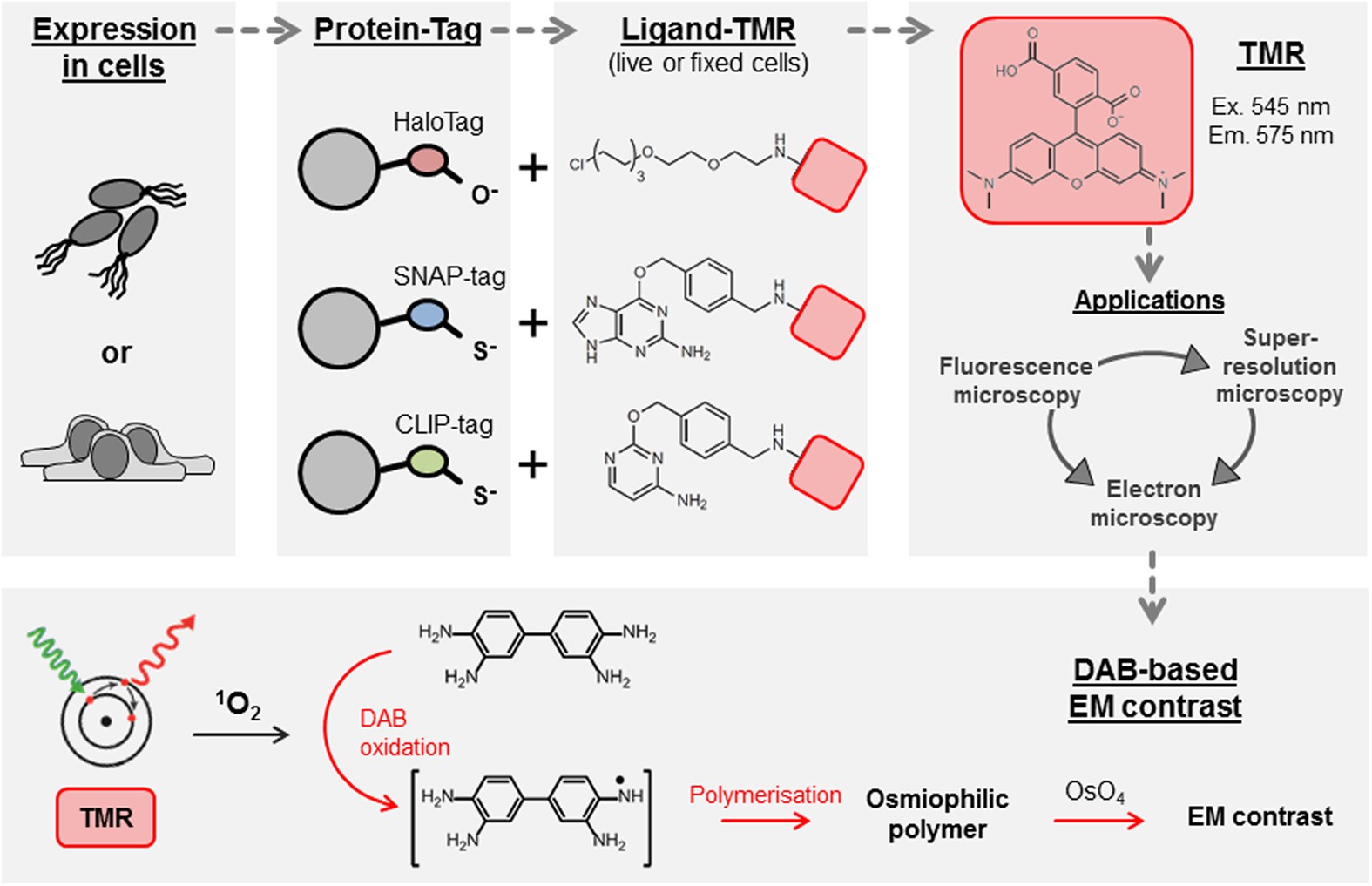
Fluorescent tag - Wikipedia S. cerevisiae septins revealed with fluorescent microscopy utilizing fluorescent labeling In molecular biology and biotechnology, a fluorescent tag, also known as a fluorescent label or fluorescent probe, is a molecule that is attached chemically to aid in the detection of a biomolecule such as a protein, antibody, or amino acid.
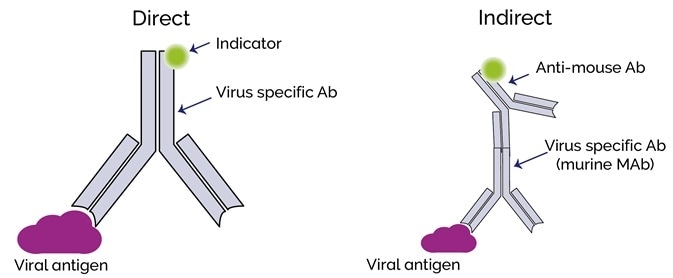
Immunolabeling for Correlative Light and Electron Microscopy on ... An ideal label for light and electron microscopy would contain both fluorescent dye and a colloidal nanoparticle on a single antibody molecule. Secondary and tertiary label, the colloidal nanoparticles are placed on the primary antibody while the fluorescent dye conjugated to secondary ( D) or tertiary ( E) antibody.
Fluorescent Nanodiamonds for HeLa Cell Drug Delivery 24.8.2022 · The developed fluorescent nanodiamonds were characterized using infrared (IR) spectroscopy, dynamic light scattering (DLS), and secondary electron microscopy. Compared to the free drug with drug release in 12 hours, the fluorescent nanodiamonds functionalized with drug molecules exhibited sustained drug release for over 72 hours.
Fluorescence Imaging - Teledyne Photometrics Fluorescent molecules (known as fluorophores) are used to label samples, and fluorophores are available that emit light in virtually any color. In a fluorescent microscope, a sample is labeled with a fluorophore, and then a bright light ( excitation light) is used to illuminate the sample, which gives off fluorescence ( emission light ).
Fluorescent Cell Stains for Organelles & Cellular Structures | Biotium MemBrite® Fix labels cells more evenly than traditional membrane stains, ... “Light-On” LysoView™ 555 “Light-On” LysoView™ 555 is a UV-activatable lysosome stain. ... Fluorescent hydrazides are formaldehyde-fixable, water soluble fluid phase tracers.
(PDF) Introduction to Microscopy - ResearchGate 8.11.2017 · 1. Microscopy with light and electrons 2. Electron/specimen interactions: processes and detectors 3. The electron microscope family 4. Specimen preparation for electron microscopy 5.
Fluorescence Microscopy vs. Light Microscopy - News-Medical.net This means that fluorescent microscopy uses reflected rather than transmitted light. For example, a commonly used label is green fluorescent protein (GFP), which is excited with blue light and...
Introduction to Fluorescent Proteins | Nikon’s MicroscopyU Continued development of fluorescent protein architecture for yellow emission has solved several of the problems with the yellow probes. The Citrine variant of yellow fluorescent protein is very bright relative to EYFP and has been demonstrated to be much more resistant to photobleaching, acidic pH, and other environmental effects. Another derivative, named Venus, is the fastest …
Label-free prediction of three-dimensional fluorescence images from ... Label-free prediction of three-dimensional fluorescence images from transmitted-light microscopy Understanding cells as integrated systems is central to modern biology. Although fluorescence microscopy can resolve subcellular structure in living cells, it is expensive, is slow, and can damage cells.
Fluorescence Microscopy - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics M. Heilemann, in Comprehensive Biophysics, 2012 Abstract. Fluorescence microscopy is a valuable toolbox to study cellular structures and dynamics spanning scales from the single molecule to the live animal. The spatial resolution that can be achieved with any light-based microscopy is however limited to about 200 nm in the imaging plane and >500 nm along the optical axis.
ZEISS Lightsheet 7 – Light Sheet Microscope Light sheet fluorescence microscopy (LSFM) is ideal for fast and gentle imaging of whole living model organisms, tissues and cells as they develop – over extended periods of time. What’s more, use ZEISS Lightsheet 7 to image large optically cleared …
PDF In Silico Labeling: Predicting Fluorescent Labels in Unlabeled Images The z-stacks of transmitted-light microscopy images were acquired with different methods for enhancing contrast in unlabeled images. Several different fluorescent labels were used to generate fluorescence images and were varied between training examples; the checkerboard images indicate fluorescent labels that were not acquired for a given example.
Imaging Flies by Fluorescence Microscopy: Principles, Technologies, and ... The development of fluorescent labels and powerful imaging technologies in the last two decades has revolutionized the field of fluorescence microscopy, which is now widely used in diverse scientific fields from biology to biomedical and materials science. ... has brought about the era of fluorescence light microscopy. The first fluorescence ...
PDF Direct Evidence of Lack of Colocalisation of Fluorescently Labelled ... Fluorescently labelled nanoparticles are routinely used in Correlative Light Electron Microscopy (CLEM) to combine the capabilities of two separate microscope platforms: fluorescent light microscopy (LM) and electron microscopy (EM). The inherent assumption is that the fluorescent label observed under LM colocalises well with the electron dense ...


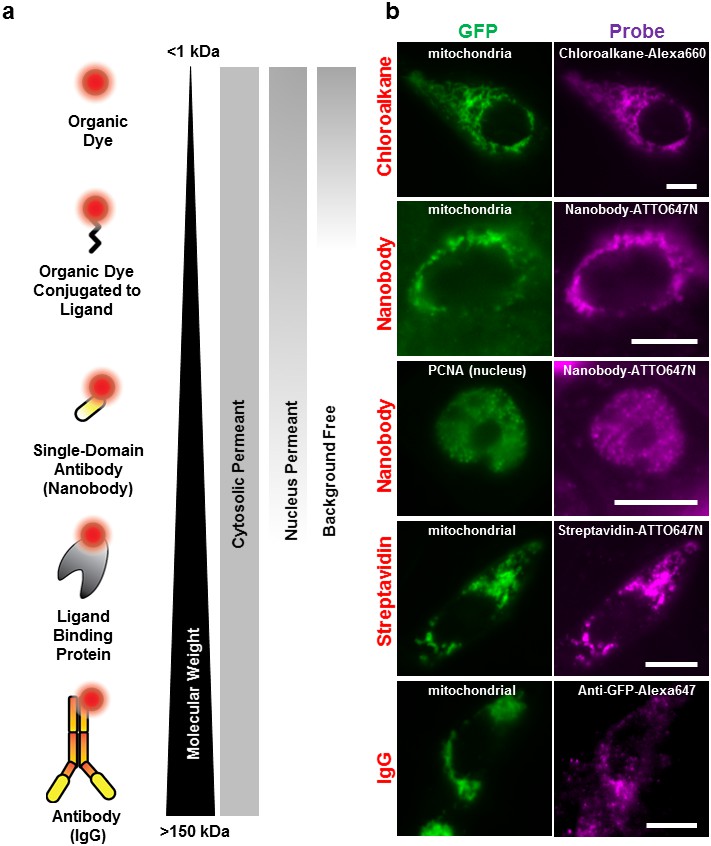


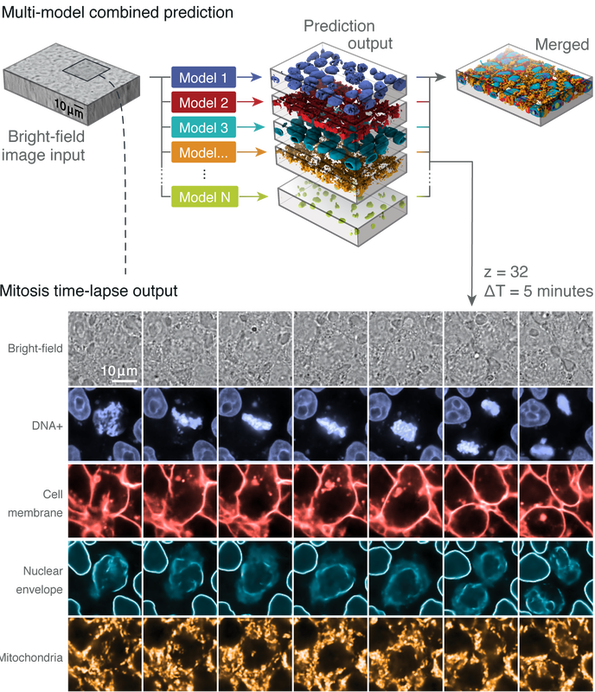













Post a Comment for "41 fluorescent labels and light microscopy"